- Published on
How to contribute to Open-Source Software with Git & GitHub

This article was originally posted on the Noteworthy blog
Table of Contents
- Open Source Software
- What is open-source software?
- Why contribute to open source?
- Why??
- Further Your Career
- To Gain Competitive Advantage
- Reduce Development Costs and Time
- Build an Awesome Portfolio
- Interact with your Mentors, experienced developers and the community at large
- How can you contribute to Open-source Software?
- What is Git and GitHub?
- Getting started: Contributing to Open Source Software with Git and GitHub.
- 1. Find an open-source project to contribute to.
- 2. Fork a repository. 🍴
- 3. Create a branch.
- 4. Cloning a repository.
- 5. Making the changes.
- 6. Add & Commit the Changes
- 7. Push the changes.
- 8. Make a Pull Request.
- Final Remarks
- What Next?
Open Source Software
What is open-source software?
Open-source software (OSS) is a type of computer software in which source code is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to study, change, and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose…
- Wikipedia.
In a nutshell, open-source software is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify, and enhance. It is mostly designed to be publicly accessible, anyone can see, modify, and distribute the code as they see fit.
From the earliest days of computers, programmers developed software through collaboration. For instance, a programmer in Kenya develops a new application, then another programmer in the Netherlands studies the application and discovers ways to improve it. The knowledge is shared, and the entire community benefits from the collective growth.
However, open-source software isn’t exactly free software, Companies may still sell services and products related to open-source software. For instance, they can offer a premium version of the software that has additional features.
Fun fact: 96% of all code contains open-source code!!
Open-source is a cornerstone of software development and its impossible to imagine a past, present or future without open-source software.
Why contribute to open source?
I have always been the person to pip install, npm install or git clone a piece of software without really thinking about the creators or maintainers. I’ve never really thought about how I can contribute to the projects and the benefits that will be pushed my way as a result of that.
What about you?
Have you ever wondered why both the largest and smallest companies greatly contribute to open-source? Have you asked yourself why most developers actively contribute to open-source?
In June of 2019, Tidelift and The New Stack jointly fielded a survey of professional software developers. It was really interesting that most developers (84%) view themselves as active contributors to open-source projects.
A similar analysis was done for companies on GitHub:
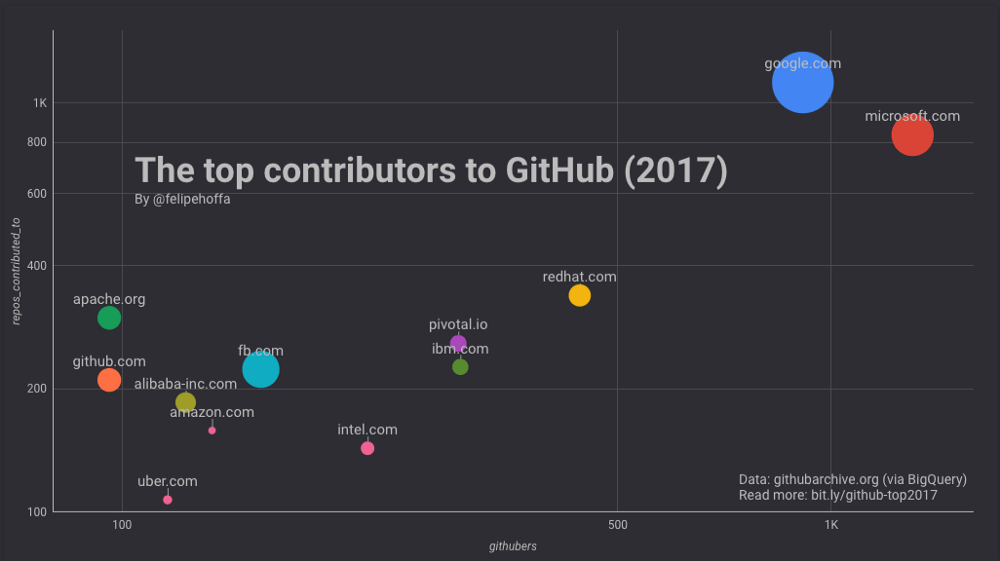 The Top 10 Companies Contributing to Open Source as per 2017. Source: whitesourcesoftware.com
The Top 10 Companies Contributing to Open Source as per 2017. Source: whitesourcesoftware.com
From the graph above, it’s pretty clear that some of the most successful and influential technology companies are serious about actively contributing to open-source.
Why??
Further Your Career
When you contribute to open source, you are recognized, you sharpen your programming skills, and become part of the vibrant community. This makes you very visible to potential employers. In a 2016 report from the Linux Foundation, 86 per cent of technology professionals said that open source had helped them thrive in their careers.
“When it comes to hiring developers, I’ll take a GitHub commit log over a resume any day.”
- John Resig
To Gain Competitive Advantage
That seems a little counter-intuitive because anyone can use open-source code. However, organizations say that when their developers are writing code for a project, they get to know the software better than those who only use it. Some companies can leverage that expertise in ways that benefit their bottom line.
Reduce Development Costs and Time
When persons or organizations open source an application that originated in-house, they can access a much larger community of developers. Instead of relying only on their team members, they get contributions from many different people who are all interested in making the software better.
Build an Awesome Portfolio
Many companies are looking to hire talent with skills related to specific open source projects, and there are few better ways to demonstrate your expertise than by actually having written some of the code for a project. Your contributions to open source projects will clearly show your skill, reliability and motivation. Open source gives you recognition.
Why do you think you are asked for your GitHub account when applying for a technical role?
Interact with your Mentors, experienced developers and the community at large
Working on an open-source project might allow you to work with some of the best creators in the world. You will now have a common interest and most likely work on it together.
How can you contribute to Open-source Software?
-
Create your own open-source project and host it somewhere public like GitHub.
-
Create open-source alternatives to commercial software.
-
Contribute to existing open-source projects. This can be done through contributing to the software, design, documentation, community or writing articles like the one you are currently reading. This is what we will be majorly focusing on in this article.
What is Git and GitHub?
Have you ever collaborated on a project or on a certain document with someone else that may be stored in someplace like Google Drive? How did you track the changes? How did you know who changed what and when? What about versions? How easy was it to collaborate? This will most likely land you in a mess. 😅😅
It must have been such a struggle to collaborate in that manner. I wouldn’t wish such on my worst enemy.
This is where Git comes in. To solve all these problems and more…
Git is a distributed version control system for tracking changes in source code during software development. It is designed for coordinating work among programmers, but it can be used to track changes in any set of files. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows.
- Wikipedia
In English, Git is a version control tool that is used to track changes in files or source code including what specifically has been changed, who has changed what and when. Git allows a team of people to work together, all using the same files. It helps the team cope with the confusion that tends to happen when multiple people are editing the same files.
Version control systems are software tools that help a software team manage changes to source code over time. Version control software keeps track of every modification to the code in a special kind of database
By far, Git is the most widely used modern version control system in the world. It is a mature, actively maintained open-source project originally developed in 2005 by Linus Torvalds, the famous creator of the Linux operating system.
GitHub, on the other hand, is an online service to which developers who use Git can connect and upload or download resources. An online hub for Git.
Founded in April 2008, GitHub is like a “ Facebook for software development”. It is a very nice platform for anyone to check out, contribute to and get involved in the open-source community. You’ll meet the creators of your favourite projects, developers, designers, project managers, e.t.c and even get to work with them.
Using GitHub regularly can help you learn how to work well in a development team environment.
GitHub is a Git hosting repository that provides developers with tools to ship better code through command line features, issues (threaded discussions), pull requests, code review, or the use of a collection of free and for-purchase apps in the GitHub Marketplace. With a collaboration community of over 15 million developers and an ecosystem with hundreds of integrations, GitHub changes the way software is built.
- GitHub.com
Getting started: Contributing to Open Source Software with Git and GitHub.
This is the most interesting part.
Prerequisites:
-
Ensure you have used a computer before this.
-
Ensure you install git.
-
Create a GitHub account.
Confirm you have Git installed by checking the version of Git installed on your device by running this command on your terminal or command line. ( Windows/Mac/Linux )
git --version
 My GitHub Profile. There is a very huge chance that the background on yours will be white.
My GitHub Profile. There is a very huge chance that the background on yours will be white.
1. Find an open-source project to contribute to.
Try to find a friend’s project or even try out one of my projects for the sake of learning. Just go to their profile then navigate to repositories.
A repository is like a folder for your project. Your project’s repository contains all of your project’s files and stores each file’s revision history. … For user-owned repositories, you can give other people collaborator access so that they can collaborate on your project. A repository is like a ‘fancy name’ for a folder.
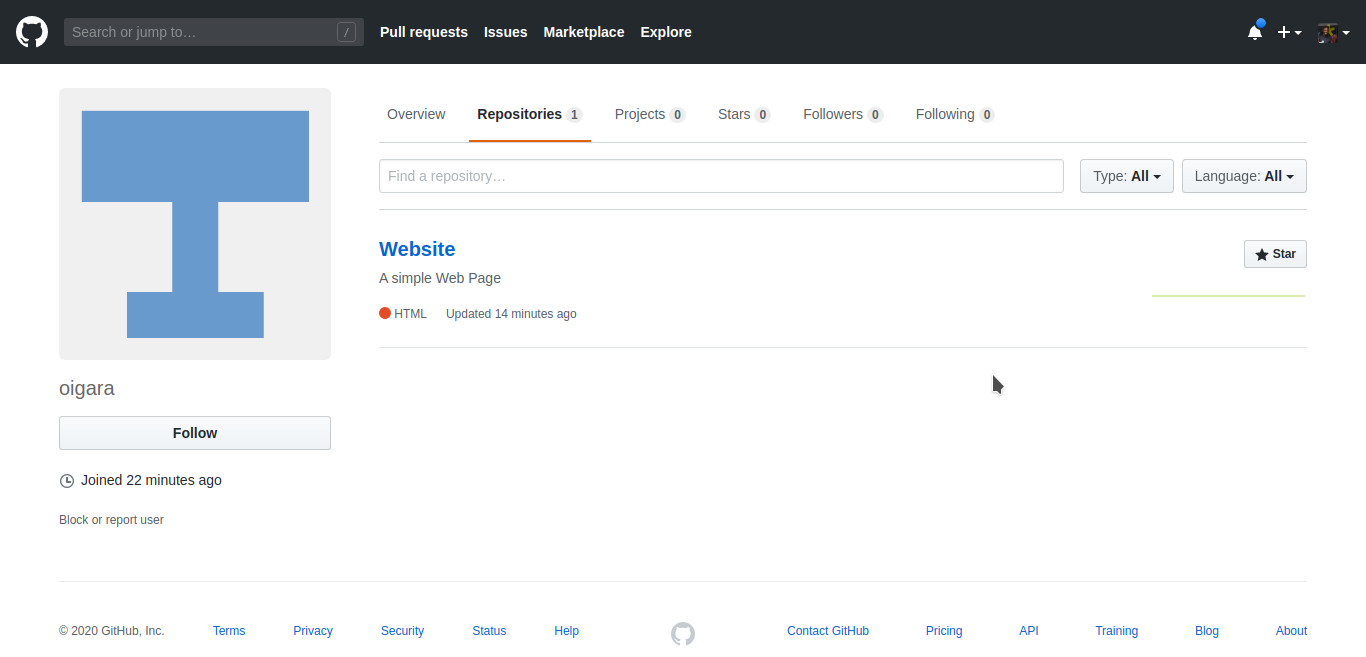
If you can see a page similar to the one above, you are good to go. 🙂
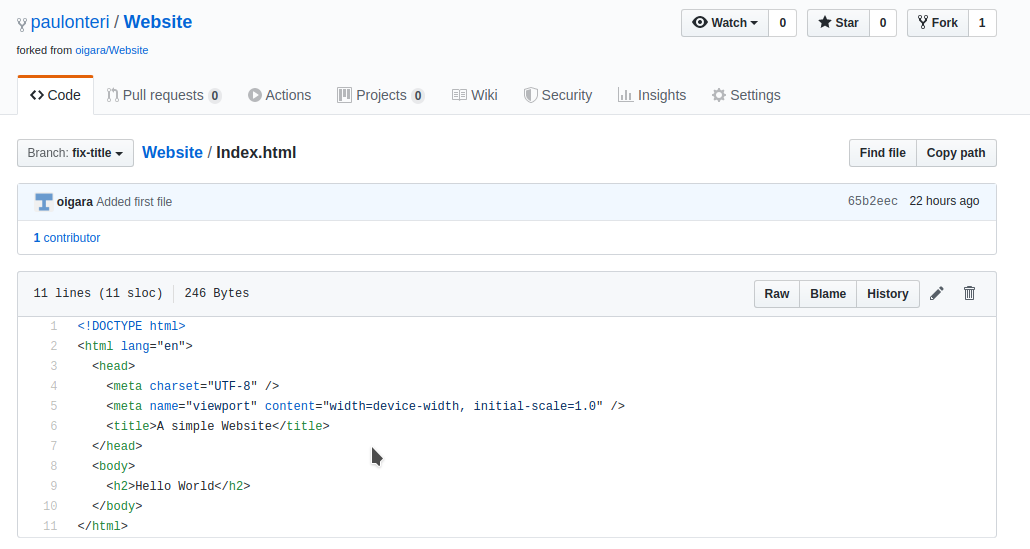
I am currently interested in the ‘Website’ repository shown above.
2. Fork a repository. 🍴
A fork is a copy of a repository. Forking a repository allows you to freely experiment with changes without affecting the original project.
When you click the fork button in GitHub, you are duplicating the entire repository and its history up until that point in time. You make a copy of the repository (the one being forked) into your own GitHub account.
How to fork a repository:
-
Navigate to the repository you want to work on and open it. ( In my case, the ‘Website’ repository from oigara’s account)
-
Click the Fork button located at the top right area of the page.
In my case, I’ll fork the website repository. It’s as simple as clicking on the Fork button as shown below.
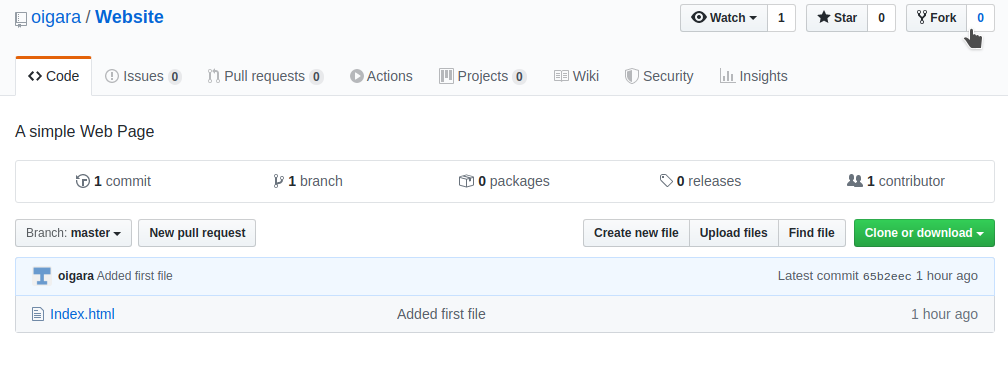
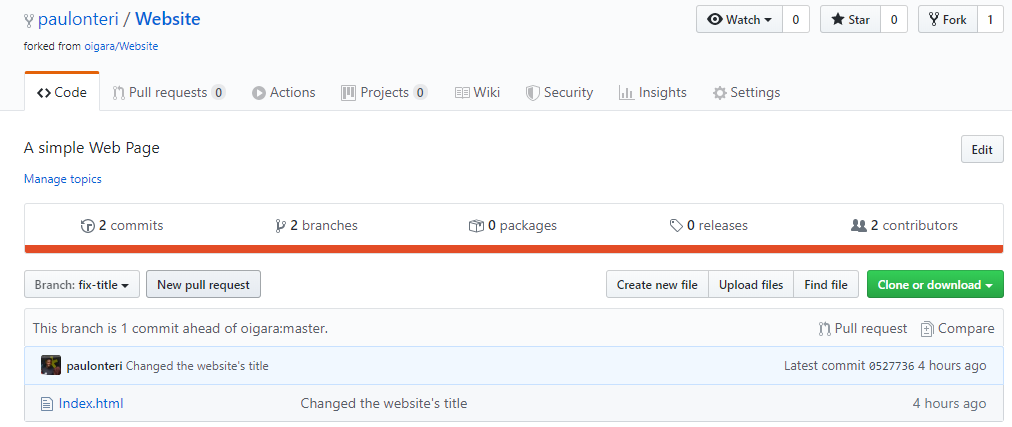
Notice that GitHub automatically navigates to your account after forking. For example, mine navigated from oigara/Website (the original account and repository) to paulonteri/Website (my account and the forked repository).
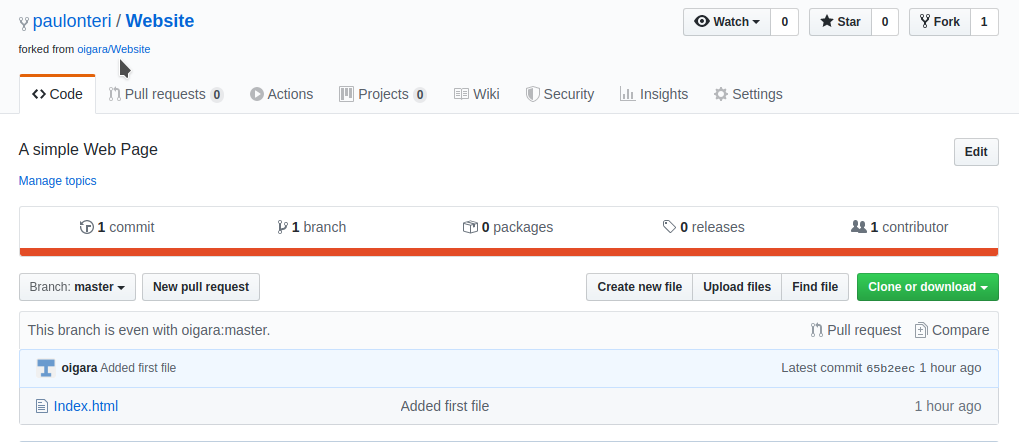
That’s it — after forking, you’ll have a copy of the original repository in your GitHub account.
3. Create a branch.
A branch is a version of the repository that diverges from the main working project. Essentially an almost new and independent line of development.
Use a branch to isolate development work without affecting other branches in the repository. Each repository has one default branch, mostly called the master branch and can have multiple other branches. It represents an independent line of development. You can think of them as a way to request a brand new working directory.
You can even create a new branch using GitHub.
How to create a new branch:
- On the main page of the repository, click the branch selector menu.
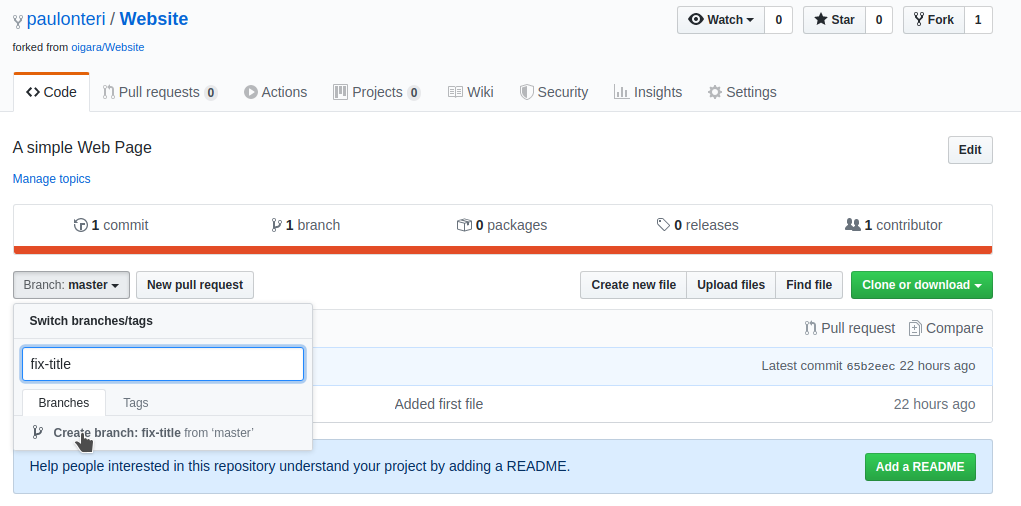
- Type in a new name for your branch then select Create branch.
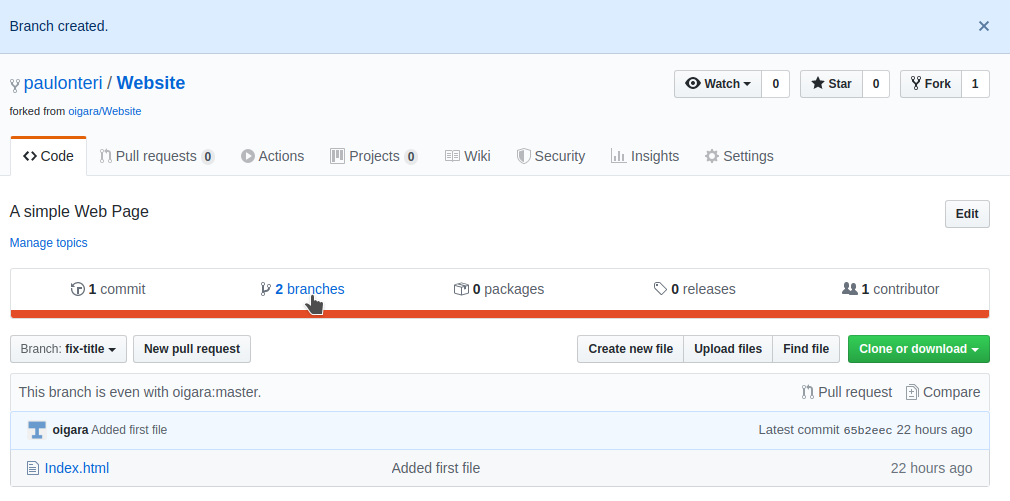
Awesome! Notice that the number of branches increased by one and the branch selector menu now shows that you are on the newly created branch. You now have a new branch.
You can proceed to work on it without affecting the master/main branch.
4. Cloning a repository.
Cloning utility which is used to target an existing repository and create a clone, or copy of the target repository.
- Atlassian.com

Cloning a repository means that you’re downloading a copy of the source code from a specific source.
Right now, you have a fork of the repository you forked, but you don’t have the files in that repository on your computer. Let’s create a clone of your fork locally on your computer.
How to clone a repository:
- Click on the green Clone or Download button in the forked repository. This will initiate a popup titled ‘Clone with HTTPS’.
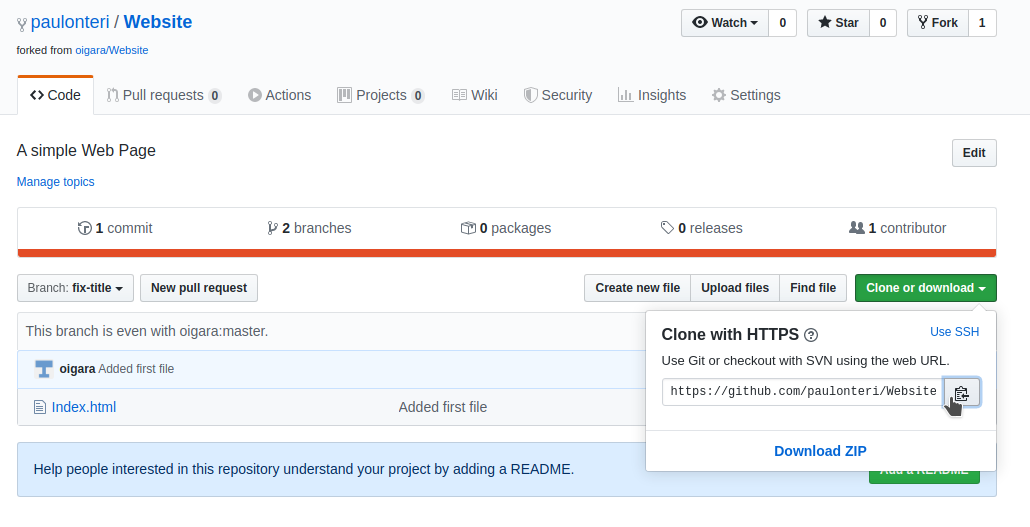
-
Copy the URL on the popup manually or by clicking on the copy button shown above.
-
Open terminal or the command line in any folder on your device.
-
Type in the command
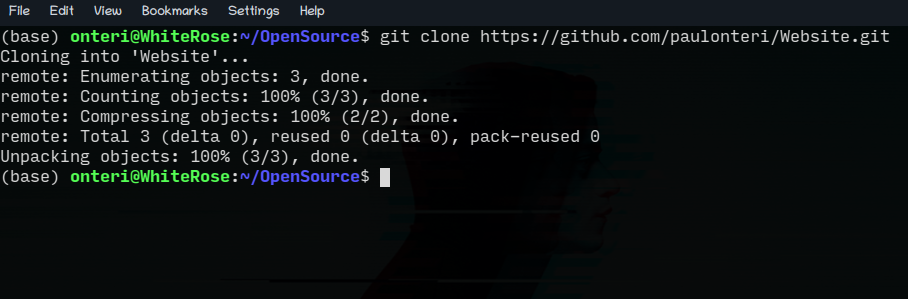
git cloneproceeded by the URL copied from the popup. In my case:git clone -
[https://github.com/paulonteri/Website.git](https://github.com/paulonteri/Website.git)
You should see output that is similar to what is below.
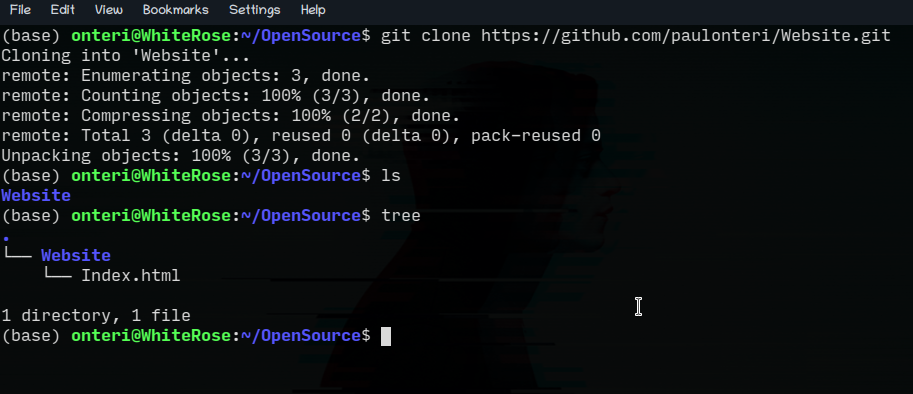
Check out what is in your folder using the ls command on a Mac/Linux and dir on a Windows device. I also use the tree command that can be installed separately.
An alternative would be to open the folder using your default file manager.
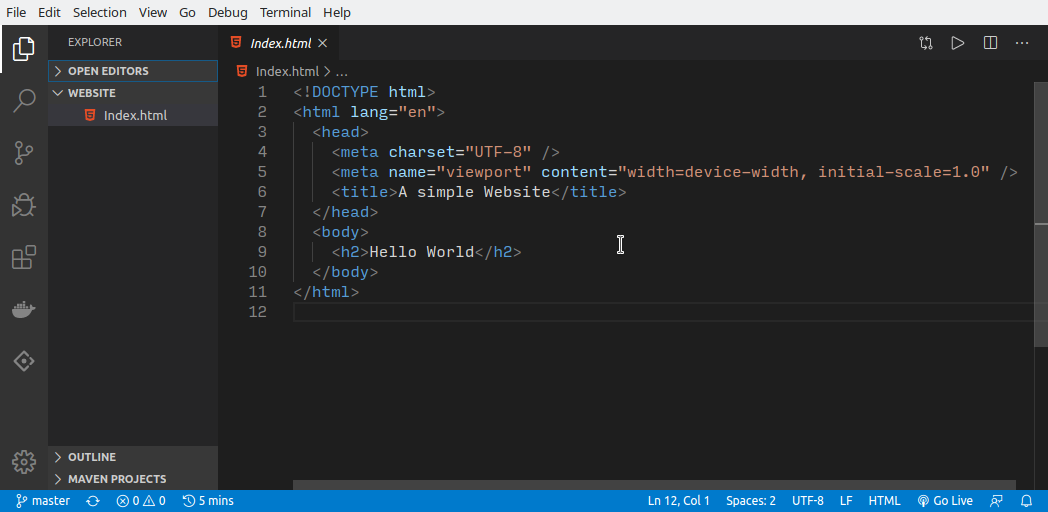
Now that you have the project files, you can freely edit them. You can open the files in a text editor of your choice and start working on them.
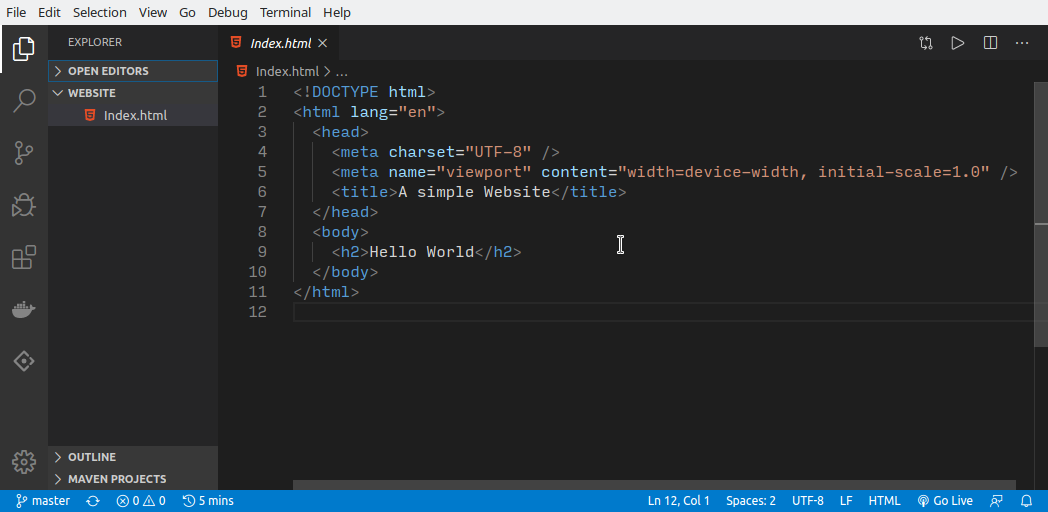
It’s awesome that you now have the content that was on your GitHub.
5. Making the changes.
This is where you now make your changes to the files.
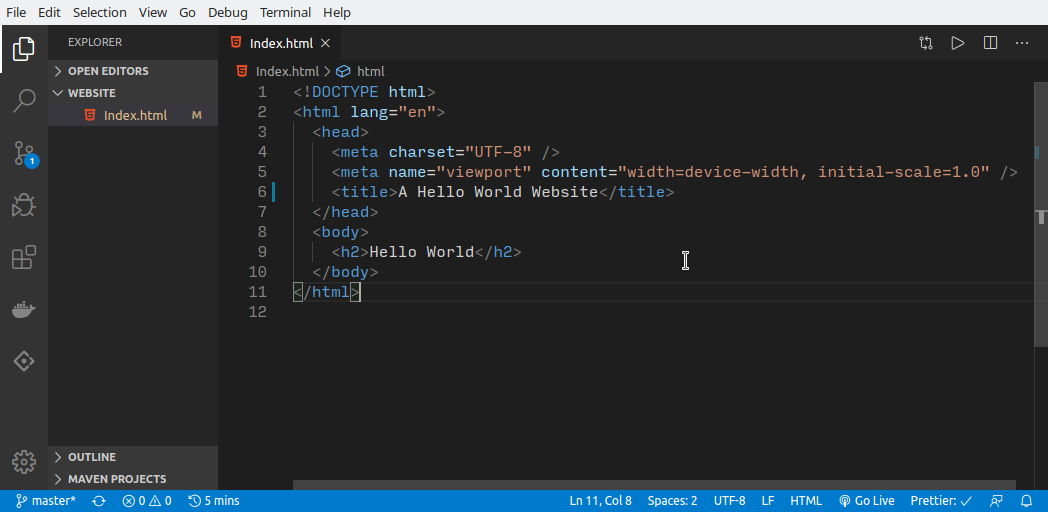
Who doesn’t love VS Code?? 😍😍😍
6. Add & Commit the Changes
The
git commitcommand will save all staged changes, along with a brief description from the user, in a “commit” to the local repository.
- guide.freecodecamp.org
The
git addis a command, which adds changes in the working directory to the staging area. With the help of this command, you tell Git that you want to add updates to a certain file in the next commit.
- w3docs.com
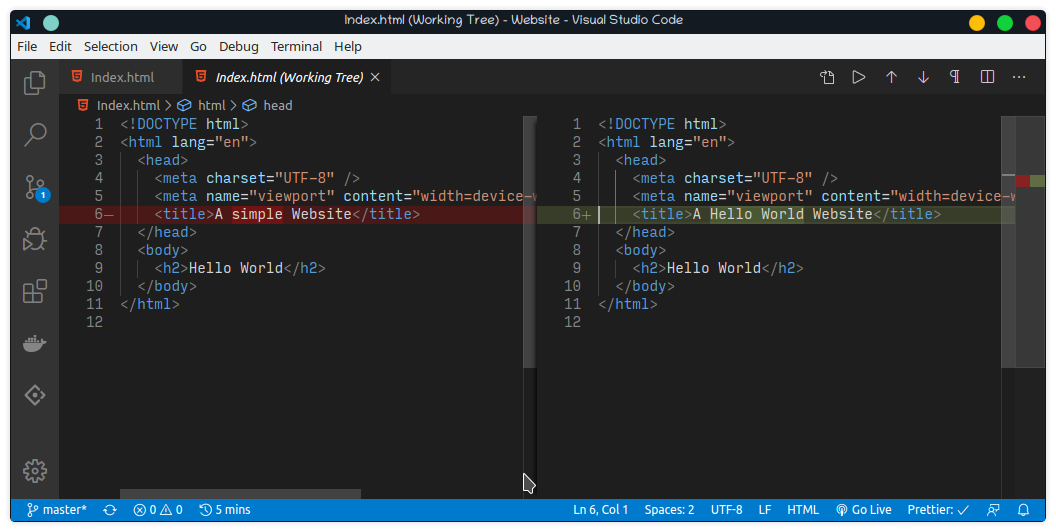
The git commit command will save the changes you made.
However, you have to explicitly tell Git which changes you want to include in a commit before running the git commit command. This means that a file won’t be automatically included in the commit just because it was changed. Instead, you need to use the git add command to mark the desired changes for inclusion.
For Example, these are the steps I took:
-
I navigated to the project’s folder using terminal(this can also be done using CMD)
-
I pulled and created locally the specific branch I want to commit to using
git pullwhich will take two arguments; the local-branch-name:remote-branch-name(GitHub remote name) which should be the same.git pull <local-branch-name>:<remote-branch-name>In my case:git pull origin fix-title:fix-titleI then moved to the specific branch I want to work on usinggit checkout.(The default branch ismaster)git checkout fix-title
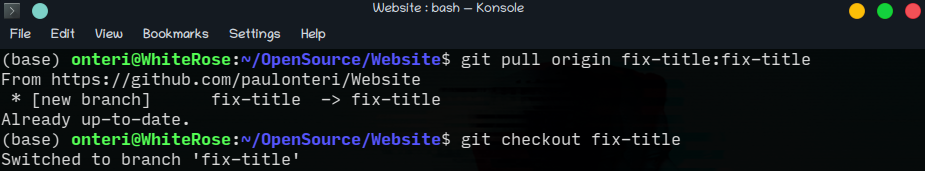
-
Then staged/added the index.html file using
git add.git add Index.html -
I then committed the changes using the
git commitcommand. I also added a short description/message of the changes made using the option-m(that stands for ‘message’) followed by my message in quotation marks" ".git commit -m “Changed the website title”
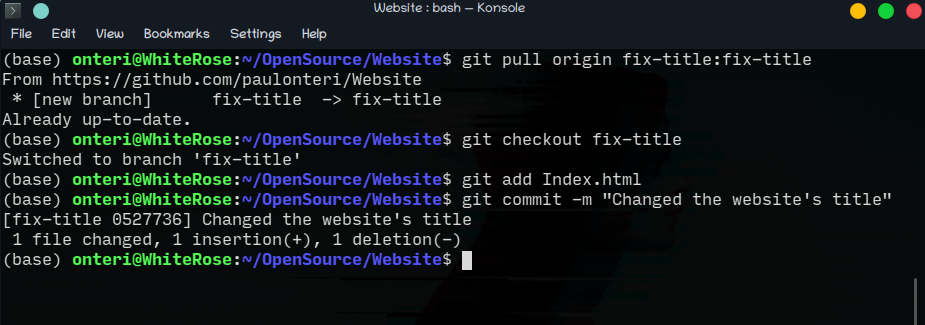
7. Push the changes.
The
git pushcommand is used to upload local repository content to a remote repository. Pushing is how you transfer commits from your local repository to a remote repository.
- Atlassian.com

Note: The
git commitcommand captures and saves the project's current changes. However, commit is not automatically transferred to the remote server, in this case, GitHub. Using thegit commitcommand only saves a new commit object in the local Git repository.
You can use git push command to upload the content of the local repository to GitHub.
The git push command takes two arguments:
-
A remote name, for example,
originthe default remote name is always ‘origin’. -
A branch name, for example,
masteror the branch you created.
git push <remote> <branch>
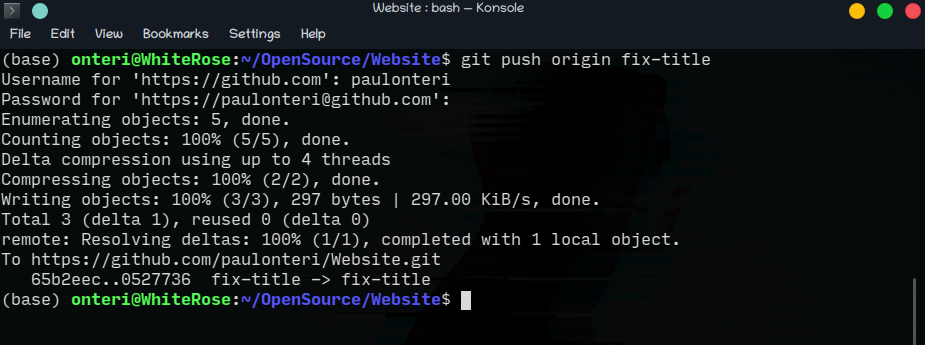
Carry out the git push command and if everything is okay so far, you will be requested for your username and password proceeded by your changes being pushed to the branch you specified on GitHub.
Your changes will now be visible on GitHub.
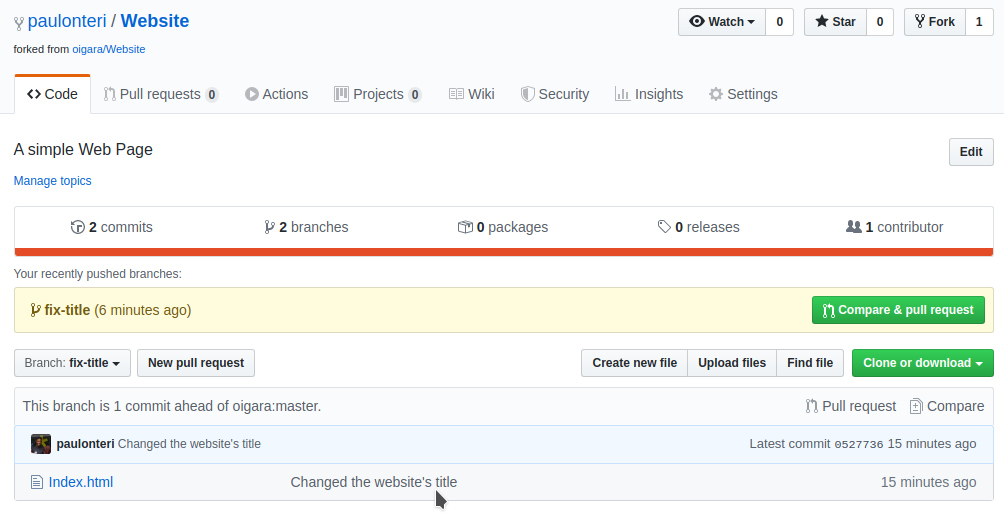
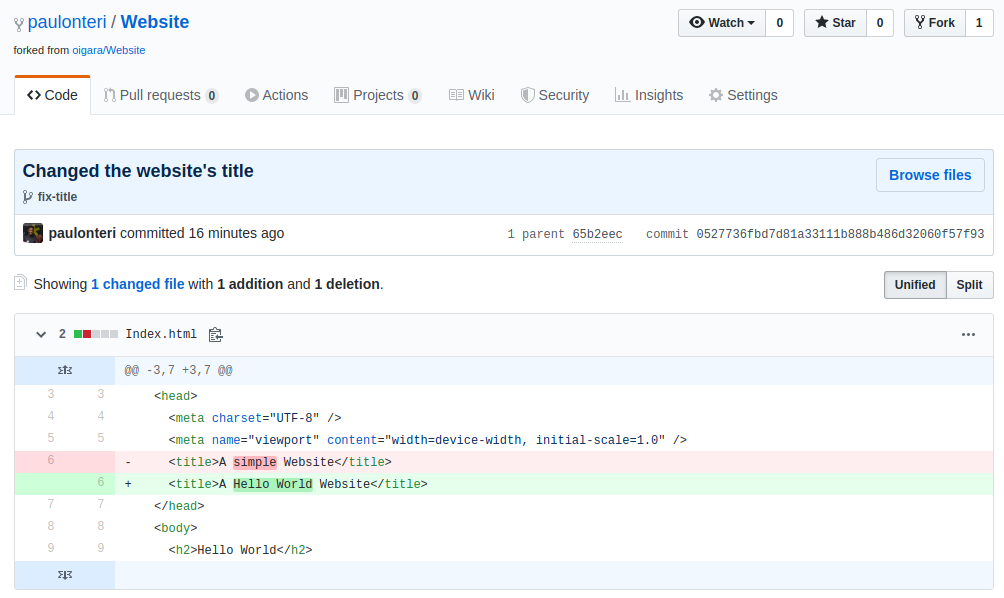
8. Make a Pull Request.
Pull requests let you tell others about changes you’ve pushed to a branch in a repository on GitHub.
Pull requests are a feature that makes it easier to collaborate with others. They provide a user-friendly web interface for discussing proposed changes before integrating them. Once a pull request is opened, you can discuss and review the potential changes with collaborators before your changes are merged into the official repository.
How to submit a pull request:
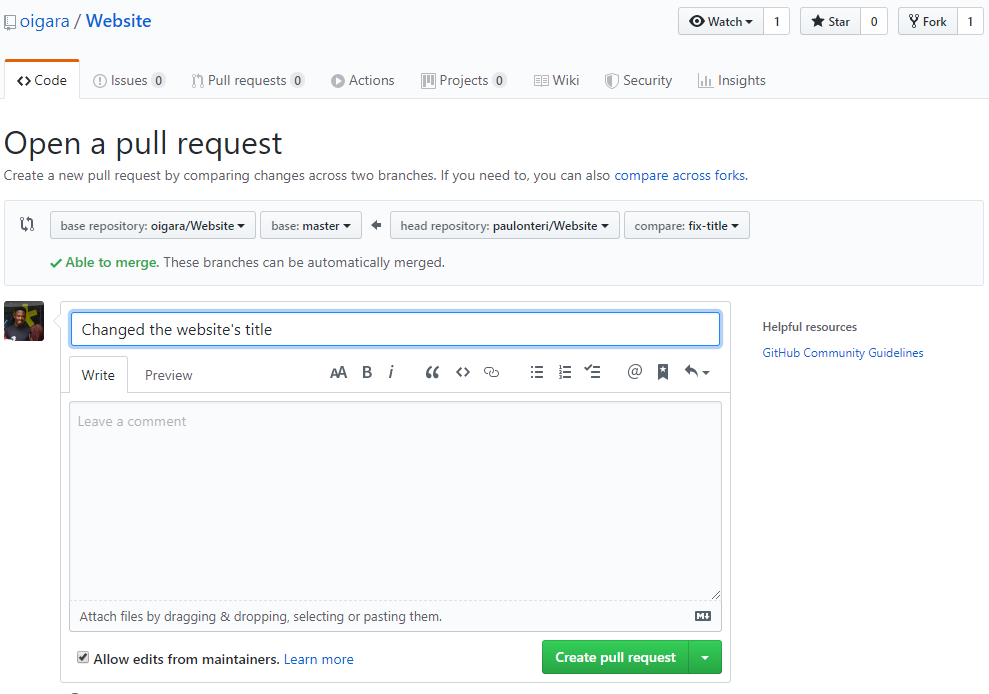
- On the repository branch you have worked on, click on the New pull request button. This will be somewhere on the left near the branch selector button. Once clicked, you’ll be taken to a new screen.
-
On the next screen, use the base branch drop-down menu to select the branch you’d like to merge your changes into, then use the compare branch drop-down menu to choose the topic branch you made your changes in. In my case, the base repository I’m merging to is oigara/website and the base branch is master.
-
It’s also nice to give a small, clear and concise title and description of the changes you’ve made.
-
To create a pull request that is ready for review, click Create Pull Request. To create a draft pull request, use the drop-down and select Create Draft Pull Request, then click Draft Pull Request.
- You’ve created a pull request. 🔥🔥 The repository’s maintainers will review your contribution. From there, they can merge it if it is good, or they may ask you to make some changes.
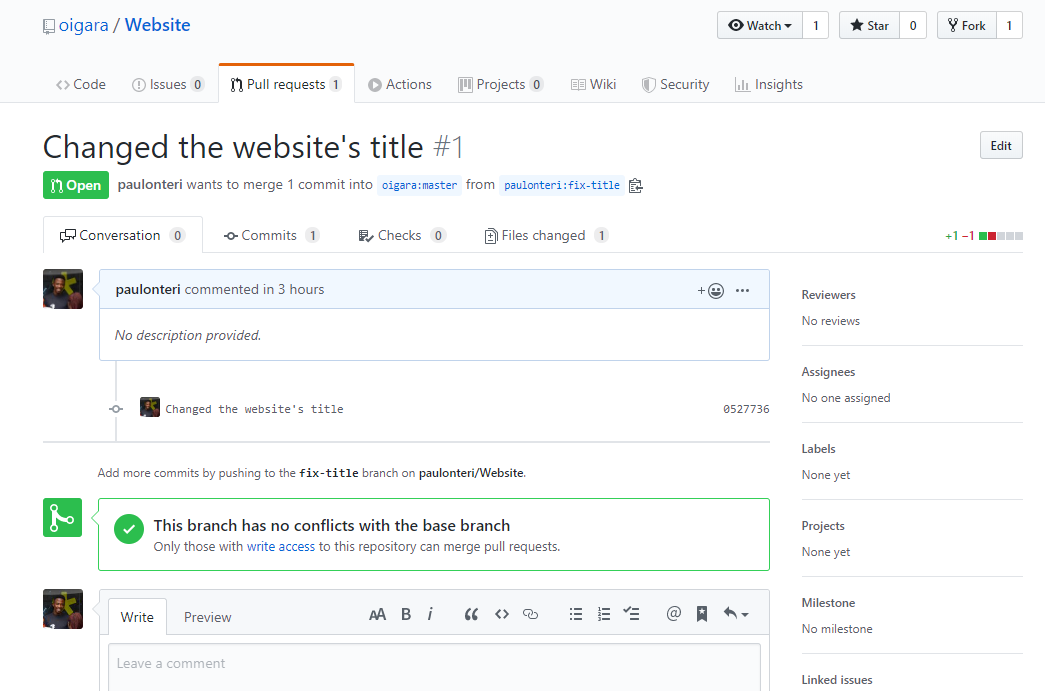
- Done. Just wait for feedback.
Final Remarks
Additional notes:
-
The first draft had over 4000 words! It was too long. I had to cut out some parts and as a result, most parts of this article aren’t fully exhausted and can(should) be separate articles. Try to research more.
-
Most of the commands I used here via terminal are accessible via easy to use buttons on most text editors.
-
Open Source is a Habit. Nurturing this habit changes your identity as a Developer - Prosper Otemuyiwa.
As I finish, I’d like to greatly thank the Open Source Festival 2020 organisers and the Open Source Community Africa. From the great speakers, wonderful keynotes, fantastic breakout sessions and the amazing content they had to offer. I learned a lot. I actually wrote most part of the first draft of this article on my flight back home from the festival.
What Next?
- Learn how to use git on your favourite text editor instead of on the command line.
- Find open-source projects that interest you and try contributing to them as often as possible.
- Continue loving VS Code.
- Try out Nigerian Jollof. I first had it this year, 2020, and it was the best!
- Let’s connect. Let’s talk Open-Source, React, Django and anything software development on Twitter and LinkedIn.
This is my first article 🙂. Please feel free to comment, share the article and offer me some feedback. Thanks for your valuable time.
- Goodbye.




